SC509 is a Z80 PIO based digital I/O card designed for Z50Bus.

Documentation
- SC500 – Series Information
- SC509 – Description
- SC509 – Assembly Guide
- SC509 – Parts List
- SC509 – Printed Circuit Board
- SC509 – Support
- SC509 – User Guide
Downloads
Kits
Examples
Description
SC509 is a Z80 PIO card designed for Z50Bus.

The module has the following features:
- Full Z80 mode 2 interrupt support (IEI/IEO daisy-chain)
- Tight address decoding
- Flexible address selection
- Two 8-bit I/O ports with handshaking
- Connector on rear edge for ribbon cable
- Connector on top edge suitable for Dupont cable
Parts List
| Reference | Qty | Component |
| PCB | 1 | SC509, v1.0, PCB |
| C1 to C3 | 3 | Capacitor, ceramic, 100 nF |
| C4 | 1 | Capacitor, electrolytic, 100 µF |
| JP1 | 1 | Header, male, 2 x 8 pin, angled |
| Jumper shunts | 6 | Jumper shunt |
| P1 | 1 | Box header, 2 x 25 pin, angled, or Header, male, 2 x 25 pin, angled |
| P2 + P4 + P6 + P8 | 1 | Box header, 2 x 13 pin, angled, or Header, male, 2 x 13 pin, angled |
| P3 + P5 + P7 + P9 | 1 | Header, male, 1 x 27 pin, angled |
| R1 | 1 | Resistor, 10k, 0.25W |
| RN1 | 1 | Resistor network, 8 x 100k, SIL, 9-pin |
| Spacer | 1 | Spacer, 10mm, M3, nylon |
| Screw (for spacer) | 1 | Machine screw, 6mm, M3 |
| U1 | 1 | 74HCT688 |
| U2 | 1 | Z80 PIO Z84C2008, or Z80 PIO Z84C2010 |
| U3 | 1 | 74HCT08 |
| IC socket 20-pin U1 | 1 | 20-pin PDIP socket |
| IC socket 40-pin U2 | 1 | 40-pin PDIP socket |
| IC socket 14-pin U3 | 3 | 14-pin PDIP socket |
Printed Circuit Board
| Supplier | Website | Ships from |
| Stephen C Cousins | Tindie | UK |
| pcb4diy | pcb4diy.de | Germany |
| pcb4diy | eBay | Germany |



User Guide
SC509 is a Z80 PIO card designed for Z50Bus.

The Z80 PIO card (SC509) provides two 8-bit parallel ports with handshaking and flexible input and output connectivity, as well as support for Z80 mode 2 interrupt daisy chaining.
Input signals are taken from both the top and the side headers.
Output signals are available on both the top and the side headers.
Input and output signals are nominally 0 volts (low/off) or 5 volts (high/on).
This card should be compatible with all Z50Bus systems.
Cards using Z80 mode 2 interrupts need to be grouped together on the backplane. These cards are linked by a daisy-chain which is incorporated into the backplane. As a result you must not leave an empty slot between any cards generating interrupts.
Details about programming a Z80 PIO can be found in the Z80 PIO datasheet (PDF).
Address
The card responds to input/output addresses matching the address set with jumpers. When a jumper shunt is fitted, that bit must be a 1 (high voltage). When the shunt is not fitted, that bit must be a 0 (low voltage).
The card occupies 4 addresses, thus address bits 0 and 1 are not included in the address decoding. The board includes place holders for bits 0 and 1 for consistency with other cards in the SC500 series. It is suggested that you remove or cut the pins for bits 0 and 1 as a reminder that they are not used.
The recommended address for this card is currently 98 hex (10011000 binary) when used as part of an SC500 system. This address is selected by fitting jumper shunts for bit 7, 4, and 3.
Several of these card can be used at the same time providing the addresses are all different.
Assembly Guide
Important note: How to modify box headers
Experienced builders can just go ahead and populate the board. There shouldn’t be any surprises to catch you out.
Getting started
This guide assumes you are familiar with assembling circuit boards, soldering, and cleaning. If not, it is recommended you read some of the guides on the internet before continuing.
First check you have all the required components, as listed in the parts list.
Before assembling it is worth visually inspecting the circuit board for anything that looks out of place, such as mechanical damage or apparent manufacturing defects.
If you have a multimeter that measures resistance or has a continuity test function, check there is not a short on the power supply tracks. Connect the probes to each terminal of one of the capacitors, such as C1. This should be an open circuit, not a short.
The picture below shows what a completed SC509 should look like.

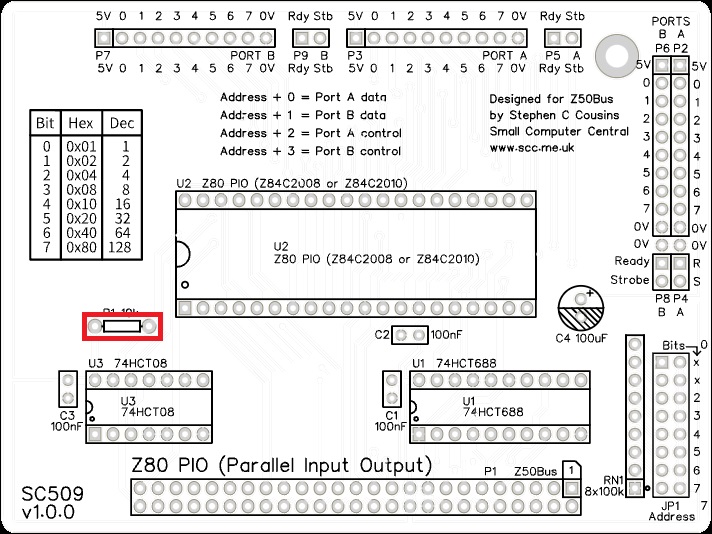
Resistor (10k)
Fit and solder the 10k resistor, R1, shown below in red.

Resistors can be fitted either way around, as they are not polarity dependent.
IC sockets
Fit and solder the IC sockets.
Be sure to fit them with the notch matching the legend on the circuit board, so you do not end up fitting the IC the wrong way around too.


Resistor networks
Fit and solder the 8x100k resistor network RN1 (shown below in red).
The 100k network will be marked 104.

Take care to fit the resistor network the correct way around. Pin 1 is usually marked with a dot. This end is indicated on the PCB and on the illustration below.


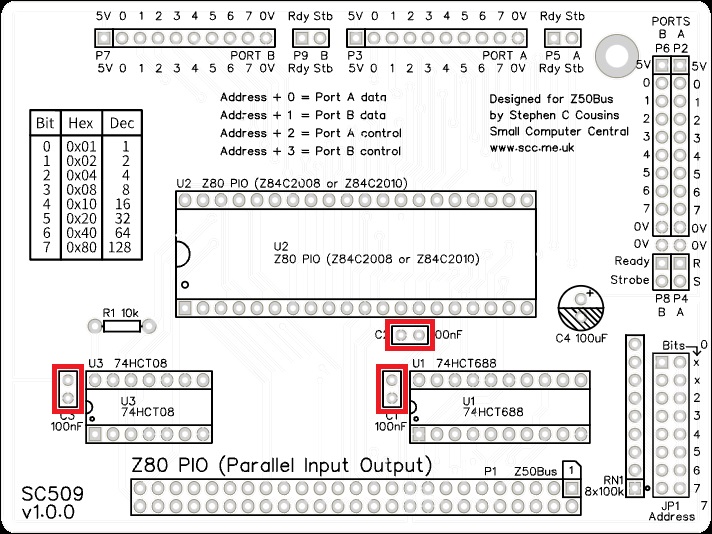
Capacitors (100 nF)
Fit and solder the 100 nF cacacitors, C1 to C3.

These can be fitted either way around as they are not polarity dependent.
The exact value of this component is not critical. The use of very cheap capacitors within the range of about 30 to 200 nF is acceptable.
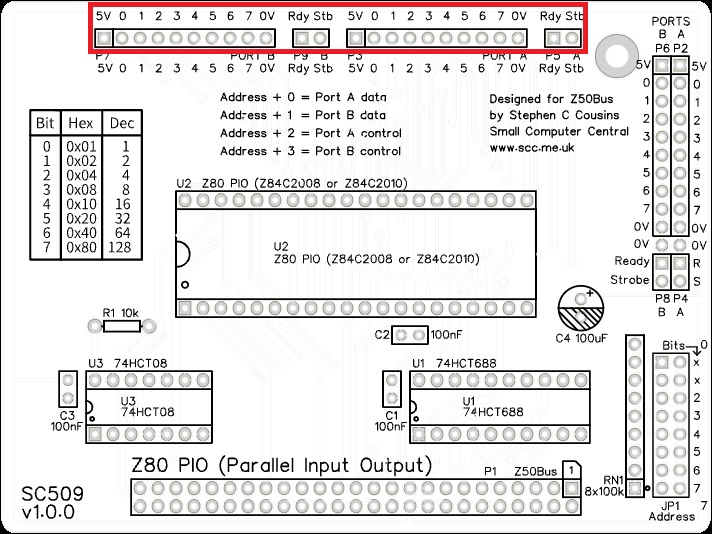
Single row angled header pins
These may need to be cut from a longer strip using wire cutters to cut the plastic.
Fit and solder the single row angled header pins, P3, P5, P7, and P9.

These can be individual short strips of header pins or one long strip with unused pins pulled out of the plastic with pliers. When pulling pins from a single row header the plastic can easily break due to the strain placed on it, so support the plastic near where the pin is being removed.
Double row angled header pins
Fit and solder the double row angled header pins, JP1.

Header JP1 is the 6 address select jumpers that are labelled with their bit numbers. The card occupies 4 addresses, thus address bits 0 and 1 are not included in the address decoding. The board includes placeholders for bits 0 and 1 for consistency with other cards in the SC500 series. It is suggested that you remove or cut the pins for bits 0 and 1 as a reminder that they are not used.

Capacitor (100uF)
Fit and solder capacitor C4.
It is important to fit this capacitor the right way around. The negative terminal is indicated with a ‘minus’ sign, as illustrated to the right. The negative terminal also has a shorter lead.

The silkscreen has a plus sign for the positive terminal and a hashed area for the negative terminal.
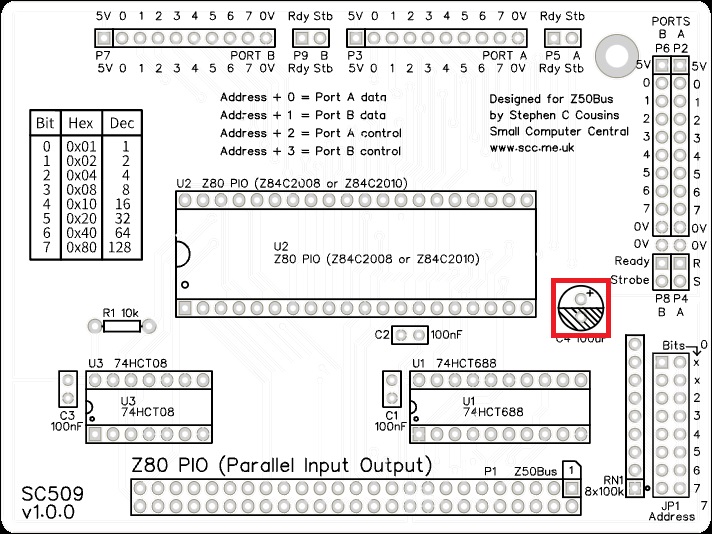
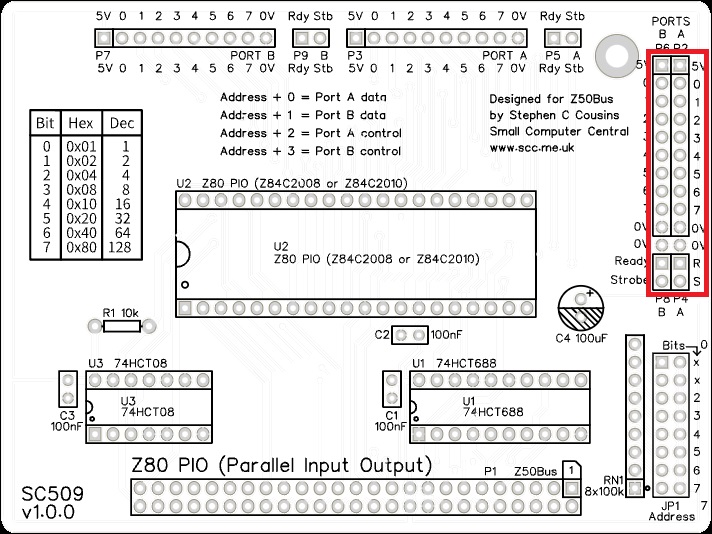
Input/Output connector
Fit and solder the I/O connector. This can either be a right angled box header or right angled header pins. The box header is recommended.


This connector incorporates four sets of signals, labelled P2, P4, P6, and P8.
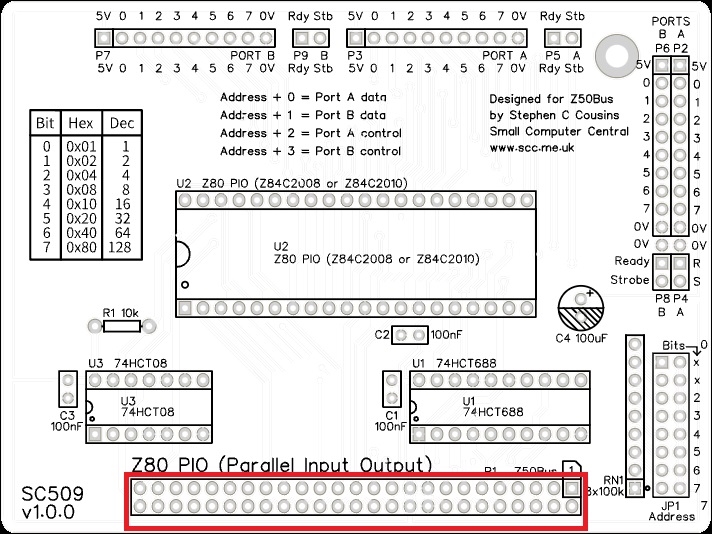
Bus connector
Fit and solder the bus connector, P1. This can either be a right angled box header or right angled header pins. The box header is recommended.


Take care to ensure the connector is fitted such that the card will stand vertically when fitted to a backplane. A good method is to just solder two pins, one at each end, and then check it looks correct. Then solder two more, one at each end but in the other row, and check again. At each stage, if necessary, adjust the position by heating the required solder joint and moving the connector slightly. Solder two pins in the middle of the connector and check again. Then solder all the others.
Inspection
Remove any solder ‘splats’ with a brush, such as an old toothbrush.
Visually inspect the soldering for dry joints and shorts.
Clean the flux off with suitable cleaning materials.
Visually inspect again. The importance of visual inspection can not be overstated.
Quick Test
Check for a short on the power supply tracks by measuring the resistance between IC U3 pin 14 and U3 pin 7 (indicated below). This should be an open circuit, not a short. If you are using a digital meter set to measure resistance it will likely take a few seconds for the reading to stabilise as there are now capacitors on the power lines. A reading of more than 100k Ω (100000 ohms) is acceptable.

Integrated circuit
Insert the integrated circuits (ICs) into their sockets, taking care to insert them the right way around, as illustrated below. Be careful not to bend any legs over.

Address select jumpers
The card responds to input/output addresses matching the address set with jumpers. When a jumper shunt is fitted, that bit must be a 1 (high voltage). When the shunt is not fitted, that bit must be a 0 (low voltage).
Header JP1 is the 6 address select jumpers that are labelled with their bit numbers. The card occupies 4 addresses, thus address bits 0 and 1 are not included in the address decoding. The board includes placeholders for bits 0 and 1 for consistency with other cards in the SC500 series. It is suggested that you remove or cut the pins for bits 0 and 1 as a reminder that they are not used.
The recommended address is currently 98 hex (10011000 binary) when used as part of an SC500 system. This address is selected by fitting jumper shunts for bits 7, 4, and 3.
You are now ready to give it a try.
Notes
- This design is made with the permission of LiNC (designers of the Z50Bus).
- This product is designed for hobby use and is not suitable for industrial, commercial or safety-critical applications.
- The product contains small parts and is not suitable for young children.